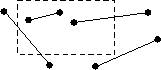
Idee von Cohen & Sutherland
Teile Ebene anhand des Clip-Fensters in 9 Bereiche ein, beschrieben durch 4-Bit-Bereichscode:
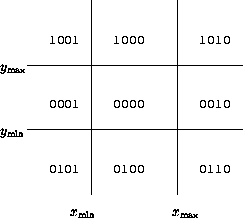
| Bit 0: | links vom Fenster |
| Bit 1: | rechts vom Fenster |
| Bit 2: | unter dem Fenster |
| Bit 3: | über dem Fenster |
Sei
![]() eine Linie.
Dann gilt bei einer bitweisen Verknüpfung:
eine Linie.
Dann gilt bei einer bitweisen Verknüpfung:
code (P1) AND code
(P2) ![]() 0
0 ![]()
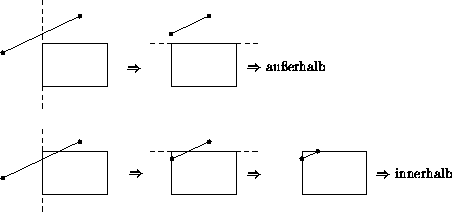
![]() komplett außerhalb (beide Punkte auf derselben Seite)
komplett außerhalb (beide Punkte auf derselben Seite)
code (P1) OR code
(P2) = 0 ![]()
![]() komplett innerhalb (beide Punkte im Clip-Fenster)
komplett innerhalb (beide Punkte im Clip-Fenster)
In den anderen Fällen wird
![]() mit einer Fensterkante
geschnitten und der Test mit der verkürzten Linie erneut ausgeführt.
mit einer Fensterkante
geschnitten und der Test mit der verkürzten Linie erneut ausgeführt.
/****************************************************************************************/
/* */
/* Clippen von Linien an einem Fenster nach Cohen-Sutherland */
/* */
/****************************************************************************************/
private static final byte EMPTY = 0;
private static final byte LEFT = 1;
private static final byte RIGHT = 2; // 4-Bit-Bereichscodes
private static final byte BOTTOM = 4;
private static final byte TOP = 8;
private int xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax; // Clip-Fensterraender
private byte region_code( // liefert den region-code
Point P ) // fuer den Punkt P
{
byte c;
c = EMPTY;
if (P.x < xmin) c = LEFT; else
if (P.x > xmax) c = RIGHT;
if (P.y < ymin) c |= BOTTOM; else
if (P.y > ymax) c |= TOP;
return(c);
}
private void set_clip_window( // setzt die Variablen xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax
Point P, // anhand des Ursprungs P des Clip-Fensters
Point delta ) // und anhand seiner Breite/Hoehe delta
{
xmin = P.x; xmax = P.x + delta.x;
ymin = P.y; ymax = P.y + delta.y;
}
private boolean cohen_sutherland( // liefert true,
Point p1, Point p2, // falls die Gerade p1-p2 sichtbar ist
Point Q1, Point Q2) // liefert ggf. sichtbaren Teil Q1-Q2 zurueck
{
boolean finite_slope; // true falls Gerade p1-p2 nicht senkrecht laeuft
double slope = 0.0; // Steigung der Geraden p1-p2
byte C, C1, C2; // 4-Bit-Bereichs-Code
Point Q = new Point(); // zu berechnender Schnittpunkt mit Gerade
Point P1 = new Point(p1); // lokale
Point P2 = new Point(p2); // Variablen
finite_slope = (P1.x != P2.x);
if (finite_slope) slope = (double)(P2.y-P1.y)/(double)(P2.x-P1.x);
C1 = region_code(P1);
C2 = region_code(P2);
while ((C1 != EMPTY) || (C2 != EMPTY)) { // mind. ein Endpunkt noch ausserhalb
if ((C1&C2) != EMPTY) return(false); // beide auf derselben Seite ausserhalb
else
{
if (C1 == EMPTY) C = C2; else C = C1; // C ist ausserhalb. Berechne
// einen Schnittpunkt mit den
// verlaengerten Fensterkanten
if ((C & LEFT) != EMPTY) { // schneide mit linker Fenster-Kante
Q.x = xmin;
Q.y = (int)((Q.x-P1.x)*slope + P1.y);
} else
if ((C & RIGHT) != EMPTY){ // schneide mit rechter Fenster-Kante
Q.x = xmax;
Q.y = (int)((Q.x-P1.x)*slope + P1.y);
} else
if ((C & BOTTOM) != EMPTY) { // schneide mit unterer Fenster-Kante
Q.y = ymin;
if (finite_slope)
Q.x = (int)((Q.y-P1.y)/slope + P1.x); else
Q.x = P1.x;
}else
if ((C & TOP) != EMPTY) { // schneide mit oberer Fenster-Kante
Q.y = ymax;
if (finite_slope)
Q.x = (int)((Q.y-P1.y)/slope + P1.x); else
Q.x = P1.x;
}
if (C==C1) {
P1.x = Q.x; P1.y = Q.y; C1 = region_code (P1);
} else {
P2.x = Q.x; P2.y = Q.y; C2 = region_code (P2);
}
}
}
// uebergib Anfang und Ende des sichtbaren Teils
Q1.x=P1.x; Q1.y=P1.y;
Q2.x=P2.x; Q2.y=P2.y;
return(true);
}