Ein selbstähnliches Objekt hat
Dimension D ,
falls es in N identische Kopien unterteilt werden kann, die
jeweils skaliert sind mit dem Faktor
r=![]() .
.
Sind N und r bekannt, läßt sich D bestimmen:
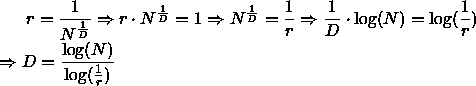
/*****************************************************************************/
/* */
/* Koch'sche Schneeflocke */
/* */
/*****************************************************************************/
private int koch_stern( // wendet eine Koch-Iteration an auf
Point poly_punkt[], // das Polygon poly_punkt
int poly_punkt_cnt) // mit poly_point_cnt Punkten
// neue Anzahl Punkte wird zurueckgeliefert
{
int i,j;
double x0,x1,x2,x3,x4,y0,y1,y2,y3,y4;
Point[] HPunkt = new Point[MAX_POINTS];
j=0;
for (i=0; i < poly_point_cnt; i++)
{
x0 = poly_punkt[i].x;
y0 = poly_punkt[i].y;
x4 = poly_punkt[(i+1)%(poly_point_cnt)].x;
y4 = poly_punkt[(i+1)%(poly_point_cnt)].y;
x1 = (x4-x0)/3+x0;
y1 = (y4-y0)/3+y0;
x3 = x4 - (x4-x0)/3;
y3 = y4 - (y4-y0)/3;
x2 = (int)(x1+ (x3-x1)*cos_60 - (y3-y1)*sin_60);
y2 = (int)(y1+ (y3-y1)*cos_60 + (x3-x1)*sin_60);
HPunkt[j] = new Point();
HPunkt[j+1] = new Point();
HPunkt[j+2] = new Point();
HPunkt[j+3] = new Point();
HPunkt[j] = poly_punkt[i];
HPunkt[j+1].x = (int)x1;
HPunkt[j+1].y = (int)y1;
HPunkt[j+2].x = (int)x2;
HPunkt[j+2].y = (int)y2;
HPunkt[j+3].x = (int)x3;
HPunkt[j+3].y = (int)y3;
j=j+4;
}
for (i=0; i < j; i++) // neu berechnetes Polygon
poly_punkt[i] = HPunkt[i]; // kopieren
return j; // neue Anzahl Punkte zurueck
}
|